Applications¶
SPSDK includes several applications which could be called directly from the command line.
Command-line applications are available in PATH after activating a virtual environment with SPSDK installed in it.
Note
See how to install SPSDK in Installation Guide chapter. If you don’t use virtual environments, the availability is not guaranteed (you’d need to add Python’s Scripts folder to PATH first).
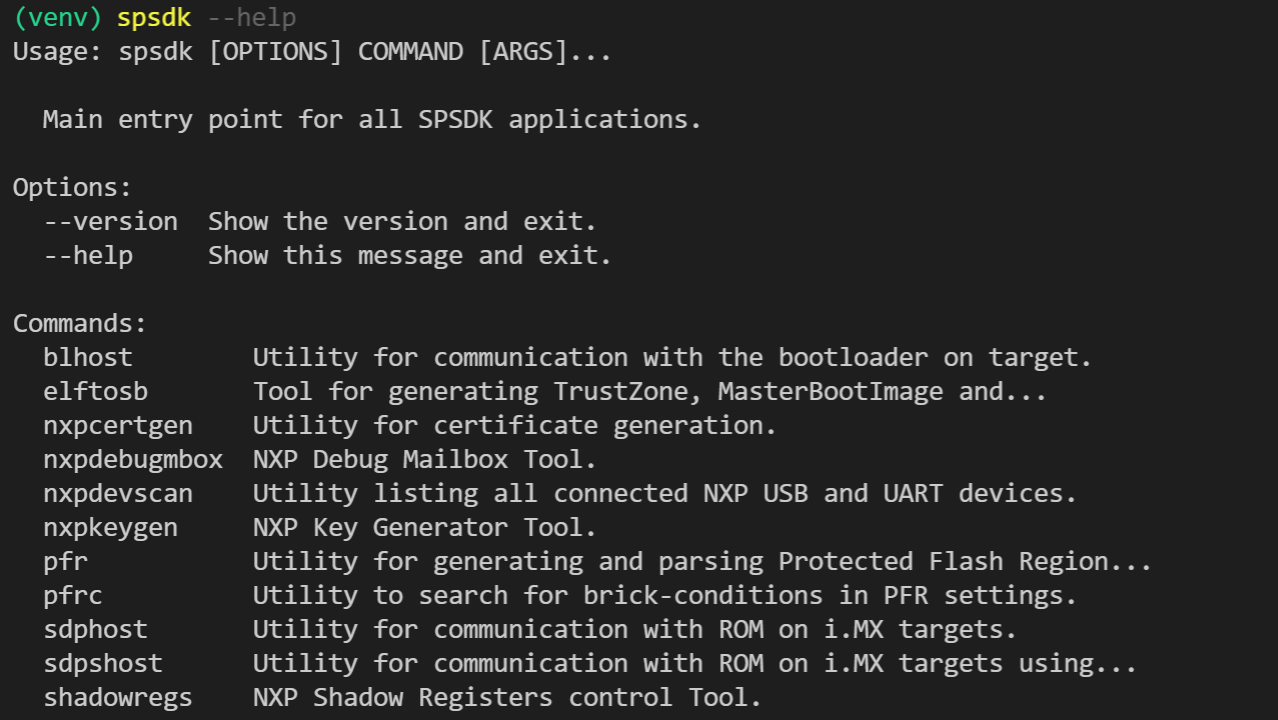
All applications could be accessed either using a special application called spsdk or directly by its name (e.g. blhost, pfr, …).
spsdk --help
Application Connectivity¶
Some applications communicate with NXP devices connected to the host PC. Details on how to configure the connectivity could be found in the following chapters:
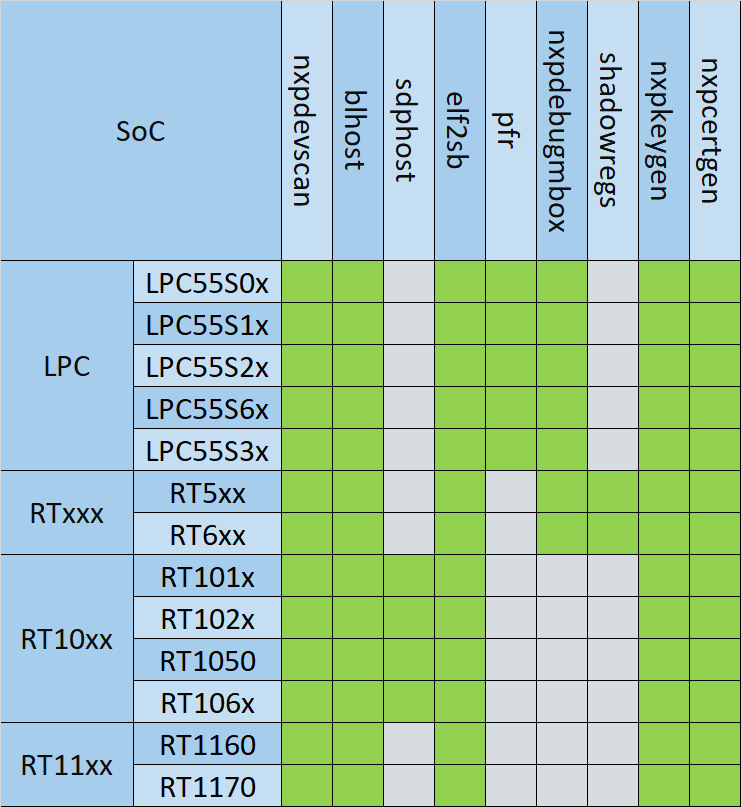
Application Overview¶
SPSDK applications are used for various functions and not all applications are valid for all NXP MCU device portfolios. The table mapping particular applications to a specific device is below.
blhost¶
The blhost application is a utility for communication with MCU Bootloader on NXP devices.
It allows user to:
apply configuration block at internal memory address to memory with ID
program one word of OCOTP Field
read one word of OCOTP Field
erase region of the flash
erase all flash according to memory id
fill memory with a pattern
get bootloader-specific property
write/read memory
reset the device
generate the Key Blob for a given DEK
receive SB file
load a boot image to the device
key provisioning
execute an application at the address
apply configuration block at internal memory address
invoke code
blhost --help
elftosb¶
The tool for generating TrustZone, MasterBootImage, and SecureBinary images.
generate TrustZone
generate MasterBootImage
generate SecureBinary
elftosb --help
nxpcertgen¶
The nxpcertgen application allows the user to generate the self-signed x.509 certificates with properties given in the JSON configuration file. The certificates are self-signed and support only BasicConstrains (ca, path_length).
nxpcertgen --help
nxpdebugmbox¶
The nxpkeygen application allows user to:
perform the Debug Authentication
start/stop Debug Mailbox
enter ISP mode
set Fault Analysis Mode
nxpdebugmbox --help
nxpdevscan¶
The nxpdevscan application allows users to list all connected USB and UART NXP devices.
nxpdevscan --help
nxpkeygen¶
The nxpkeygen application allows user to:
generate RSA/ECC key pairs (private and public) with various key’s attributes
generate debug credential files based on YAML configuration file
nxpkeygen --help
pfr¶
The pfr application is a utility for generating and parsing Protected Flash Region data (CMPA, CFPA).
It allows user to:
generate user configuration
parse binary and extract configuration
generate binary data.
generate HTML page with brief description of CMPA/CFPA configuration fields
list supported devices
pfr --help
pfrc¶
The pfrc application is a utility for searching for brick-conditions in PFR settings.
Warning
THIS IS AN EXPERIMENTAL UTILITY! USE WITH CAUTION !!!
pfrc --help
sdphost¶
The sdphost application is a utility for communication with ROM on i.MX targets.
It allows user to:
get error code of the last operation
jump to the entry point of the image with IVT at a specified address
write a file at the address
read one or more registers
sdphost --help
sdpshost¶
The sdpshost application is a utility for communication with ROM on i.MX targets.
It allows the user to write boot image data from the provided binary file.
Warning
THIS IS AN EXPERIMENTAL UTILITY! USE WITH CAUTION !!!
sdphost --help
shadowregs¶
The shadowregs application is a utility for Shadow Registers controlling.
It allows user to:
save the current state of shadow registers to the YML file
load new state of shadow registers from YML file into the microcontroller
print all shadow registers including their current values
print the current value of one shadow register
set a value of one shadow register defined by parameter
reset the connected device
print a list of supported devices
shadowregs --help